
Table of contents
Pull Up Method or Fields
Code Smells
- Several classes have the same fields / methods
- Objects offer a built-in mechanism for simplifying such situations through inheritance
Sometimes this similarity remains unnoticed until classes have been created : an inheritance structure will be created later.
Technique
Remove the fields / methods from subclasses and move it to the superclass
- Make sure fields / methods are used for the same needs in subclasses
- If the fields have different names :
- Give them the same name and replace all references to the fields in existing code
- Create a field with the same name in the superclass
- Note that if the fields/methods were private, the superclass field should be protected
- Remove the fields/methods from the subclasses
Practice
- Open
Eventindealing.with.generalizationpackage - Pull Up everything that needs to be pulled from children classes
package dealing.with.generalization;
public class Concert extends Event {
private boolean running;
private long startTime = 0;
private long stopTime = 0;
private int volume = 30;
private final String description;
public Concert(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public void start() {
if (running) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Concert is already in progress");
}
this.startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
running = true;
}
public void stop() {
if (running) {
running = false;
stopTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
public long getElapsedTime() {
return running ? (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) : (stopTime - startTime);
}
public void volumeUp(int increase) {
this.volume += increase;
}
public void volumeDown(int decrease) {
this.volume -= decrease;
}
}
public class TheaterPiece extends Event {
private boolean running;
private long startTime = 0;
private long stopTime = 0;
private final String description;
private final int numberOfActors;
public TheaterPiece(String description, int numberOfActors) {
this.description = description;
this.numberOfActors = numberOfActors;
}
public void start() {
if (running) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Concert is already in progress");
}
this.startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
running = true;
}
public void end() {
if (running) {
running = false;
stopTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
public long calculateElapsedTimes() {
return running ? (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) : (stopTime - startTime);
}
}
Shortcuts
- Highlight stuff you want to pull up then :
- Then Right Click
- Select
Refactor | Pull members Up - Select everything you want to pull
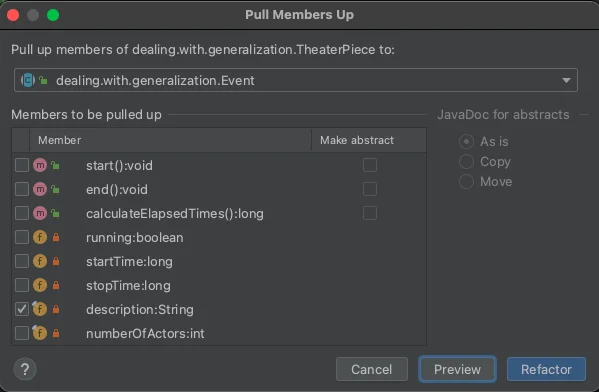
- More info here
Benefits
- Eliminates duplication
- More cohesive classes
Drawbacks
N/A
Extract Superclass
Code Smells
- Several classes with common fields and methods/behaviors
- Objects offer a built-in mechanism for simplifying such situations through inheritance
Sometimes this similarity remains unnoticed until classes have been created : an inheritance structure will be created later.
Technique
- Create an abstract superclass
- Use Pull Up Field, Pull Up Method, and Pull Up constructor Body to move the common functionality to a superclass
- Start with the fields
- Since in addition to the common fields : you will need to move the fields that are used in the common methods
- Look for places in the client code where use of subclasses can be replaced with your new class (such as in type declarations)
Practice
- Open
CustomerandProspectindealing.with.generalizationpackage - Create a base Superclass
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Customer {
private final String name;
private final String email;
private final String phone;
private final LocalDate creationDate;
private final LocalDate conversionDate;
private final List<String> messages;
}
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Prospect {
private final String name;
private final String email;
private final String phone;
private final LocalDate creationDate;
private final List<String> messages;
}
Shortcuts
- Right Click in the file
- Select
Refactor | Extract Superclass - Follow the instructions
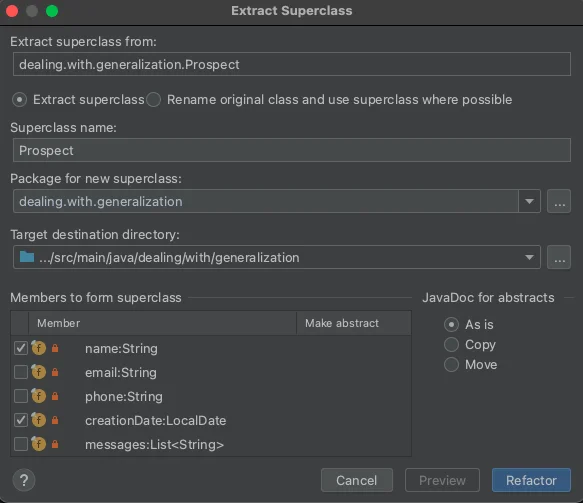
- More info here
Benefits
- Code deduplication
- Common fields and methods now live in only one place
Drawbacks
- Cannot apply this technique to classes that already have a superclass
Extract Interface
Code Smells
- Several classes are declaring the same behaviors or/and properties
- Parts of several classes are the same
Technique
- Create an empty interface
- Declare common operations in the interface
- Declare the necessary classes as implementing the interface
- Change type declarations in the client code to use the new interface/abstraction
Extracting an interface allows isolating only common interfaces, not common code. If classes contain Duplicate Code, extracting the interface won’t help you to deduplicate.
Practice
- Open
TriAthleteandJumpyAthleteindealing.with.generalizationpackage - Extract a common Interface
- Use this new Interface in the client code (tests)
@AllArgsConstructor
public class TriAthlete {
private final String name;
public void swim() {
System.out.println(name + " started swimming");
}
public void cycle() {
System.out.println(name + " started cycling");
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(name + " started running");
}
}
@AllArgsConstructor
public class JumpyAthlete {
private final String name;
public void swim() {
System.out.println(name + " started swimming");
}
public void cycle() {
System.out.println(name + " started cycling");
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(name + " started running");
}
public void jump() {
System.out.println(name + " is skydiving");
}
}
Shortcuts
- Right Click in the file
- Select
Refactor | Extract Interface - Follow the instructions
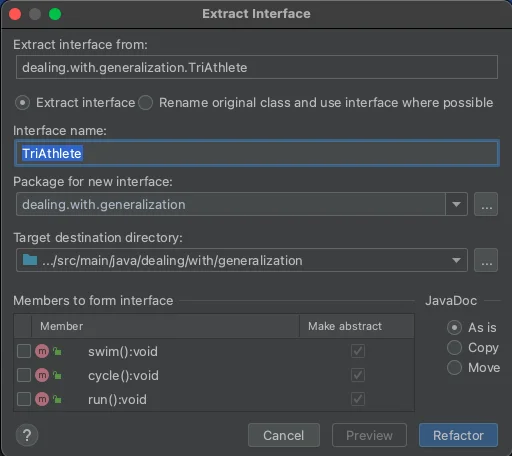
- More info here
Benefits
- More explicit code
- Small interfaces (check Interface Segregation Principle from S.O.L.I.D Principles)
Drawbacks
N/A
BONUS : Use default interface to refactor this code
 Skip to main content
Skip to main content