
Table of contents
Consolidate Conditional Expression
Code Smells
- Multiple conditionals that lead to the same result or action
Technique
- Consolidate the conditionals in a single expression by using AND and OR As a general rule when consolidating
- Perform Extract Method on the operator conditions and give the method a name that reflects the expression’s purpose
Practice
- Open
AuthorizationServiceinsimplifying.conditional.expressionspackage - Simplify if else
public class AuthorizationService {
public boolean isAuthorized(User user, String action) {
if (action == null) {
return false;
}
if (action.equals("")) {
return false;
}
if (user.getAge() < 18) {
return false;
}
if (user.isDisabled()) {
return false;
}
if (!user.isLoyal()) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
Before touching this kind of code always check the Code Coverage
- Let’s cover the missing branch
- Only then simplify if else
Benefits
- Eliminates duplicate control flow code
- More readable code
- By consolidating all operators
- Isolate the complex expression in a method with a name that explains the conditional’s purpose
Drawbacks
- N/A
BONUS : what do you think about the tests ? / Would you favor mocks over instantiating concrete objects ?
Consolidate Duplicate Conditional Fragments
Code Smells
- Identical code in all branches of a conditional
Technique
- Move the code outside of the conditional :
- If the duplicated code is
at the beginningof the conditional branches- Move the code to a place before the conditional
- If the code is
at the endof the branches- Place it after the conditional
- If the duplicate code is
randomly locatedinside the branches- First try to move the code to the beginning or end of the branch
- Depending on whether it changes the result of the subsequent code
- If the duplicated code is
- If appropriate, and the duplicate code is longer than one line, try using Extract Method.
Practice
- Open
PriceCalculatorinsimplifying.conditional.expressionspackage - Identify duplication
- Remove duplicate code by using your IDE
@AllArgsConstructor
public class PriceCalculator {
private final boolean isSaleDay;
public double calculatePrice(double price) {
double total;
if (isSaleDay) {
total = price * 0.5;
notifySales(total);
} else {
total = price * 0.98;
notifySales(total);
}
return total;
}
private void notifySales(double amount) {
}
}
Shortcuts
- Put your cursor on the if line and use this shortcut (
Show intention actions and quick-fixes)
| IntelliJ |
|---|
| Alt+Enter |
| ⌥+↩ |
Benefits
- Code deduplication
Drawbacks
- N/A
Decompose Conditional
Code Smells
- Complex conditional
if...elseswitch
- The longer a piece of code is the harder it is to understand.
Technique
- Decompose the complicated parts of the conditional into separated methods :
- The condition : then and else
- Use your
Extract Methodfeature
- Repeat the process for each block
Practice
- Open
RoomPriceCalculatorinsimplifying.conditional.expressionspackage - Decompose conditional by extracting methods
@AllArgsConstructor
public class RoomPriceCalculator {
private static final LocalDate HIGH_SEASON_START_DATE = LocalDate.of(LocalDate.now().getYear(), 6, 30);
private static final LocalDate HIGH_SEASON_END_DATE = LocalDate.of(LocalDate.now().getYear(), 10, 31);
private final LocalDate today;
private final double regularPrice;
private final double highSeasonRate;
private final double lowSeasonRate;
private final double lowSeasonExtraCharge;
public double calculatePriceFor(int numberOfRooms,
LocalDate selectedDate) {
double price;
if (selectedDate.isAfter(today) && (selectedDate.isBefore(HIGH_SEASON_START_DATE) || selectedDate.isAfter(HIGH_SEASON_END_DATE))) {
if (numberOfRooms <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid Number of Rooms");
}
price = numberOfRooms * regularPrice * lowSeasonRate + lowSeasonExtraCharge;
} else if (selectedDate.isAfter(today)) {
price = numberOfRooms * regularPrice * highSeasonRate;
if (numberOfRooms <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid Number of Rooms");
}
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Selected date should be in the future");
}
return price;
}
}
Shortcuts
Extract method :
| IntelliJ | Eclipse |
|---|---|
| Ctrl+Alt+M | Alt+Shift+M |
| ⌘+⌥+M | ⌥+⌘+M |
Benefits
- More maintainable / understandable code
Drawbacks
- N/A
Replace Conditional with Polymorphism
Code Smells
- Conditional which performs various actions depending on object type or properties
Technique
- Create subclasses matching the branches of the conditional
- Create a shared method and move code from the corresponding branch of the conditional to it
- Then replace the conditional with the relevant method calls
Practice
- Open
Calculatorinsimplifying.conditional.expressionspackage - Extract behaviors into class hierarchies
public class Calculator {
public static int calculate(int a, int b, String operator) {
int result;
if ("add".equals(operator)) {
result = a + b;
} else if ("multiply".equals(operator)) {
result = a * b;
} else if ("divide".equals(operator)) {
result = a / b;
} else if ("subtract".equals(operator)) {
result = a - b;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not supported operator");
}
return result;
}
}
Shortcuts
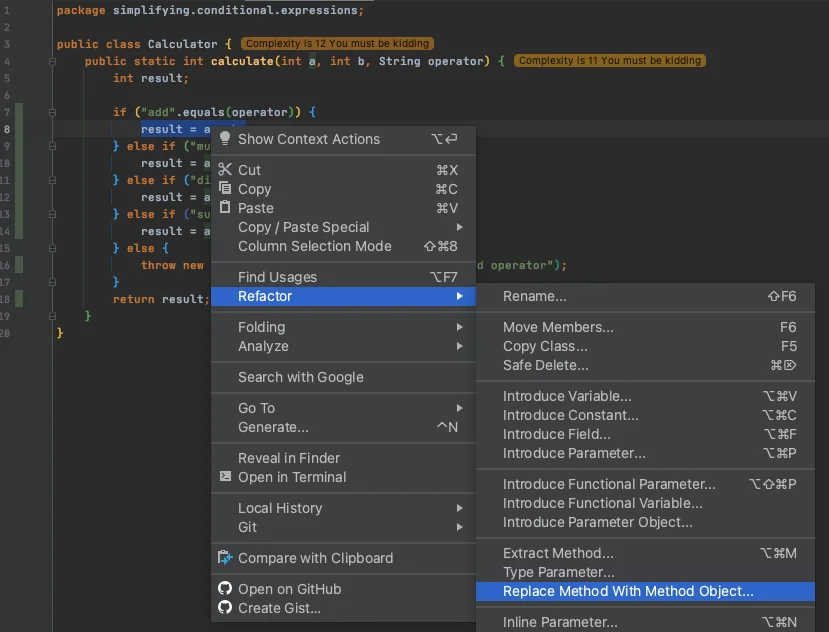
Replace Method with Method Object by using Refactor | Replace Method with Method Object menu in IntelliJ
Benefits
- If you need to add a new execution variant
- All you need to do is add a new subclass without touching the existing code (Open/Closed Principle)
- Adheres to the Tell-Don’t-Ask principle :
- Instead of asking an object about its state and then performing actions based on this
- Much easier to simply tell the object what it needs to do and let it decide for itself how to do that
Drawbacks
- N/A
 Skip to main content
Skip to main content